Light streaming through leaves is more than just a pretty sight-it’s the engine that keeps you, and everything around you, alive. The process behind this is called photosynthesis, and it’s the reason you have food to eat and air to breathe. In a world without photosynthesis, life as you know it would disappear. Let’s break down what photosynthesis is, how it works, and why it’s the foundation of your daily life.
What Is Photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is the process green plants, algae, and some bacteria use to turn sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into food and oxygen. This simple-sounding reaction is the starting point for almost all energy in the living world. Without it, there would be no apples, no rice, no forests, no oxygen-and no you.
Why Photosynthesis Matters to You
Every bite of food you eat comes from photosynthesis, directly or indirectly. Plants make sugars through photosynthesis, and those sugars become the building blocks for everything from fruits to grains to the meat from animals that eat plants.
Every breath you take is possible because photosynthesis releases oxygen as a byproduct. Without it, there would be almost no oxygen in the atmosphere.
Fossil fuels like coal, oil, and gas are made from ancient plants that stored energy from photosynthesis millions of years ago2.
The Science Behind Photosynthesis
The Basic Equation
Here’s the core reaction in simple terms:
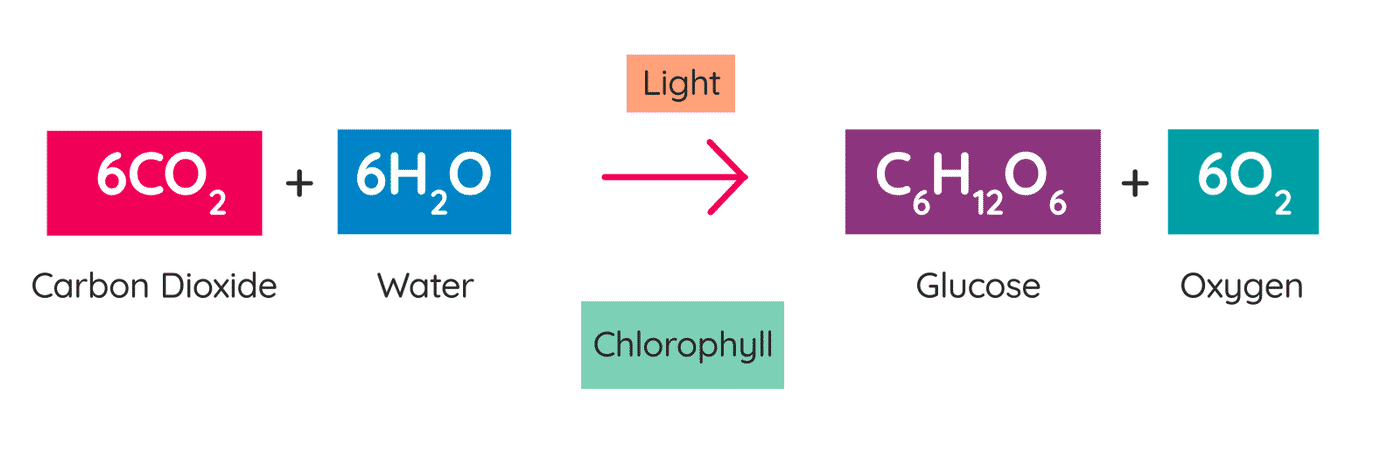
Image Credit – Studyclix.ie
- Carbon dioxide (CO₂) from the air
- Water (H₂O) from the soil
- Light energy from the sun
These combine in plant leaves to make glucose (a sugar) and oxygen (O₂).
Where Does Photosynthesis Happen?
Chloroplasts are tiny structures inside plant cells where photosynthesis takes place. Chlorophyll is the green pigment that captures sunlight and gives plants their color.
Two Main Stages of Photosynthesis
1. Light-Dependent Reactions
Take place in the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplasts.
Sunlight is absorbed by chlorophyll, splitting water molecules into oxygen, protons, and electrons.
This stage produces energy-rich molecules (ATP and NADPH) and releases oxygen.
2. Light-Independent Reactions (Calvin Cycle)
Occur in the stroma of the chloroplasts.
ATP and NADPH are used to convert carbon dioxide into glucose, which stores energy for later use.
Types of Photosynthesis
- C3 Photosynthesis: Most common; takes place in the majority of plants.
- C4 Photosynthesis: Used by some plants in hot, dry environments to be more efficient.
- CAM Photosynthesis: Used by desert plants to save water.
How Photosynthesis Shapes Your World
Food Chains Start Here
Plants are called “producers” because they make their own food through photosynthesis. Animals eat plants, and other animals eat those animals. Every food chain starts with photosynthesis.
Oxygen for Life
Almost all the oxygen in the atmosphere comes from photosynthesis. Your brain, muscles, and every cell in your body need oxygen to work. Plants and algae keep the air breathable.
Energy for Today and Tomorrow
The energy in fossil fuels comes from ancient photosynthesis.
Modern solar panels are inspired by the way plants capture sunlight.
Photosynthesis and the Environment
Balancing Carbon Dioxide
Plants absorb carbon dioxide, helping slow climate change.
Cutting down forests reduces the planet’s ability to absorb CO₂.
Clean Energy
Algae and plants are being studied as sources for renewable biofuels.
Understanding photosynthesis helps scientists find new ways to produce clean energy.
How You Benefit from Photosynthesis Every Day
- Eating: Every fruit, vegetable, and grain is a direct product of photosynthesis. Even meat and dairy come from animals that eat plants.
- Breathing: The oxygen in every breath is a gift from plants.
- Materials: Wood, cotton, paper, and many medicines start as products of photosynthesis.
- Climate: Forests and fields act as natural air filters, absorbing carbon dioxide and cooling the planet.
Simple Ways to Support Photosynthesis
- Grow plants at home or in your community.
- Protect green spaces and support reforestation.
- Reduce waste and recycle to help keep the planet healthy.
Quick Facts
- Chlorophyll is the pigment that makes plants green and captures sunlight.
- Photosynthesis is responsible for nearly all life on Earth.
- The process helps regulate the climate by absorbing carbon dioxide.
FAQs
1. What is photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is the process plants use to turn sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into food (glucose) and oxygen.
2. Why is photosynthesis important for humans?
It provides the oxygen you breathe and the food you eat.
3. Where does photosynthesis happen in plants?
Inside cell structures called chloroplasts, mainly in the leaves.
4. What is the main product of photosynthesis?
Glucose, a type of sugar that stores energy.
5. What gas is released during photosynthesis?
Oxygen.
6. Do all plants use photosynthesis?
Most plants, algae, and some bacteria use photosynthesis, but not all living things do.
7. How does photosynthesis help the environment?
It removes carbon dioxide from the air and releases oxygen, helping balance the atmosphere.
8. Can photosynthesis happen without sunlight?
No, sunlight is essential for the process.
9. What is chlorophyll?
A green pigment in plants that captures light energy for photosynthesis.
10. How does photosynthesis affect climate change?
By absorbing carbon dioxide, plants help slow global warming.
Photosynthesis is more than a science topic-it’s the reason you’re here. Every meal, every breath, and every green space around you is powered by this process.

